










Dr David Szpilman

15 Brazilians die from drowning Brazilian Strategic Plan for Aquatic Safety
every day




The content, microdata tabulated and published are the registered intellectual property of SOBRASA. It should be shared to help understand the burden and reduce the problem, as long as the source referenced. In









































SOBRASA Lifesaving Society
DROWNINGS What's happening? year 2024 Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition
partnership with:
1 Bulletin 2024

This bulletin addresses the issue of drowning in all its significance, focusing on key scenarios and diverse audiences, presenting customized solutions based on scientific research published by the Brazilian Lifesaving Society - SOBRASA. The final outcome is the presentation of a Brazilian Strategic Water Safety Plan with 5 steps, meeting the 10 recommended items by the United Nations and the World Health Organization for reducing drownings.

“To solve a problem, we must first see it, admit it, and fully understand it”
Szpilman e Palacios 2017




Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
10 items recommended by the United Nations and World Health Organization to reduce drowning and SOBRASA actions.
United Nations & WHO SOBRASA Actions
4 estratégias para redução dos afogamentos
Strengthen public education through communication
Daily posts to 220,000 followers
Promote multi-stakeholder collaboration +40 Institutional Partnerships
Develop a Brazilian Strategic Plan for Water Safety
Prevention elaborated through data collection and scientific studies
This document is updated annually
SOBRASA Publications and Recommendations
6 Interventions for Drowning Reduction
Install water access barriers
Provide safer places for preschoolers
Teach water safety to school children
Train the public in Water Safety
Define and enforce safe navigation
Build resilience and manage flood risk




Pool + Safe Program
Home + Safe Program
Kim at School and Pool + Safe Programs
Surf-Save and Water safety Emergencies Programs
Navigate and Safe and Boat Programs
Municipality more Drowning Resilient Program


















Preventing drowning: an implementation guide. World Health Organization. 2017.
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa

PROBLEM SOLUTION

2
Investigate and understand the drowning problem at the international, national, regional and local levels.

3
Gathering institutions and organizations involved in the problem and solution, reinforcing unity, and providing assistance to multiply volunteers in the fight.

4

Educating the population about the risks of drowning and its solutions. Daily posts on social media reaching 220,000 followers and specific actions in mainstream media (TV, radio, and newspapers).

5
Free and customized prevention programs for the public (from simple to complex) – "a shoe for every foot.”.





BRAZILIAN STRATEGIC PLAN - SOBRASA
& RE-EVALUATE
ACT
5
1 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
IMPORTANT NOTE: COVID-19

Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic and the social distancing required by the Brazilian population as of March 2020, there was an increase in the length of stay in residences and a reduction in the frequency of water leisure areas. This disrupted the supervision of lifeguards in these public areas.


As a RESULT, drowning mortality increased in 2020, and decreased again in 2021 and 2022.

Conclusion: Increased time spent at home has led to a higher risk of fatal drownings among children aged 1 to 9. Although the frequency of visits to public water areas (beaches and rivers) was lower, the absence or reduction of lifeguards in these locations has contributed to the rise in the number of deaths among the age group that frequented these areas.






Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM

SUMMARY 2024 (base year 2022)

Every 90 min a Brazilian die by drowning (5,488 per year).



2 teenagers die daily



Men die on average 6 times more.

40% of drowning deaths occur before the age of 29.
EVERY DAY 3 children dies by drowning.





6
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM

SUMMARY 2024 (base year 2022)
Every 2 days ONE child dye by drowning at home.


Children under 10 years old and adults' dye by drowning more in natural waters (rivers, dams and beaches).

Children under 9 years old drown more often in pools and residential areas..





65% of deaths in children under 9 years of age occur in residential settings.
41% Occur
In the summer (Dec to Mar)
Children aged 4 to 12 who know how to swim are more likely to drown due to suction from pool pumps








7
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM SUMMARY 2024 (base
year 2022)



Every 2 days a TOURIST dies in Brazil
Tourists from São Paulo (20%) and Minas Gerais (8%) die in other states, 10% in Santa Catarina and 7% in Bahia.
Considering the exposure time, drowning has 200 times higher risk of mortality compared to transportation incidents.

A 48% reduction in drowning mortality over 28 years (19952022) points in the right direction in the fight against this endemic.
North of Brazil has the highest risk of drowning death

Each drowning death costs Brazil
US$ 42,424.24
IS DROWNING AN ACCIDENT?
"Drowning is not an accident, it doesn't happen by chance, it has prevention, and this is the best form of treatment"
Szpilman, 2005.
DROWNING IS AN INCIDENT!







8
AC AM RR AP PA RO TO Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM SUMMARY 2024 (base
year 2022)

Brown and Black people account for 68% of drowning deaths (population of 55%)



The indigenous population has a 3.5 times higher risk of death than browns and blacks.
48% of Brazilians who drown have 4 to 11 years of schooling
63% of people who drown are SINGLE
618
Brazilians suffered trauma from diving in shallow waters (2022)






9
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM SUMMARY 2024
(base year 2022)


For every 10 drowning deaths of Brazilians, 9 occur before reaching the hospital.

Even great swimmers can drown when they don't respect their limits or because of a sudden reduction in their water competence.
The estimated risk of drowning death in a bathing area without lifeguards is 60 times higher.

For every 18 rescues performed by lifeguards, 1 requires hospital care.


For every 38 drowned patients treated at the hospital, 1 dies.
1.Szpilman D; Near-Drowning and Drowning Classification: A proposal to stratify mortality based on the analysis of 1,831 cases. CHEST; VOL 112; ISSUE 3;1997.
2.Szpilman D, Oliveira RB, Mocellin O, Webber J. Is drowning a mere mater of resuscitation? Resuscitation 129 (2018) 103-106.
3.Venema AM, Groothoff JW, Bierens JJLM. The role of bystanders during rescue and resuscitation of drowning victims Resuscitation 2010;81(4):434–439.
4.Szpilman D, Bierens JJLM, Handley AJ, Orlowski JP. Drowning: Current Concepts N Engl J Med 2012;366:2102-10




10
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa

THE DROWNING PROBLEM SUMMARY 2024 (base year 2022)
300
deaths due to natural disasters in Brazil (2021)


5,531 Drowning deaths in Brazil (2021).
Drowning mortality in the year
2021 was 18 times higher than all disasters combined.







11
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
THE DROWNING PROBLEM
SUMMARY 2024 (base year 2022)



More than 90% of drowning deaths occur from: IGNORING THE RISKS, NOT RESPECTING PERSONAL LIMITS, and/or NOT KNOWING HOW TO ACT.


Check out the WHO page, discussing World Drowning Prevention Day

All together for a cause PARTICIPATE!




12
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa

Become a volunteer and help save lives through prevention programs.




13










INDEX Why the fight against drowning? How to plan drowning interventions? The Drowning Problem in the World 16 4 15 17 19 21 30 48 The drowning problem in Brazil The Drowning Problem – Who, When, Where and How? The Drowning Problem - Socioeconomic Assessment Understanding, Planning and Intervening – examples Swimming pool and house; Beaches; Rivers, Lakes and Dams, and Floods 53 SOBRASA – who are we? About this Bulletin and References 57 Programs & Tools SOBRASA Collaborators 14 DROWNING Prevent or regret, which side will you be on? Szpilman, 2011 In partnership with: DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 31 Municipalities and States Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
Why the fight against drowning?

5,488
Brazilians Dye by drowning in 2022 NON-FATAL incidents are estimated to be as high as 100,000. Our young people, unfortunately, are the biggest victims of this situation, as drowning is the one of the 4 main causes of death among 1 and 24 years old.

"It was only a few seconds, how could it happen so fast?"
Drowning happens in the blink of an eye and the result can be tragic.

With the growth in the number of people who enjoy the liquid environment, whether for bathing, water sports, transportation, or work; on beaches, swimming pools, rivers and lakes, it has become essential to act in favor of the prevention of this tragedy that is Drowning!
SOBRASA, WHO ARE WE?
Non-profit organization (NGO) created in 1995 with the mission of "Uniting Brazil to reduce drownings", utilizing over 15 educational, sports, recreational, cultural, and educational programs throughout Brazil for this purpose. Founded in 1995, it is the first national entity of its kind in all of South America, representing Brazil in the International Lifesaving Federation - ILS and partnering with the World Health Organization in the fight against drowning worldwide. It has a board of directors representing the 27 states of our federation, consisting of 13 directors, 56 department heads, 200 consultants, and over 90,000 collaborators in the water safety field. Its 4,000 volunteers carry out more than 13 in-person drowning prevention actions daily in various parts of Brazil and communicate with our 220,000 followers on social media Everyone works voluntarily without receiving fees or reimbursement for expenses

OUR MISSION
Unite Brazil to reduce drownings.
OUR VISION
A world without drownings.
OUR VALUES
Reliability - Determination
Altruism - Proactivity - Generosity







15
Learn more... Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
How to Plan Drowning Interventions?
Timeline

1 Understanding the Drowning Problem
Aquatic Scenery, Age Range, Gender, Water Activity, Factor precipitant, time, season, etc.
2 3
Plan interventions
Consider triggers, actions, interventions, and actors.
Implement and re-evaluate
Preparedness, Prevention, Reaction and Mitigation.


For every problem, there is a customized solution


"PREVENTION
Vilela & Szpilman, 2014





16
IS SAVING EDUCATING TO AVOID DROWNING“
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
DROWNING PROBLEM in the World (1) – WHO 2017*
One of the diseases with the greatest impact on global health and the economy.
• Drowning data worldwide are underestimated by 5 to 10 times (SOBRASA estimation)
• In 2015, out of 192 WHO member countries, only 40% reported drowning data (grey areas on the map)
235,000 deaths per year

SOBRASA estimates that there are more than 500,000 in the world.


50% of all deaths occur under the age of 25.
World map of drowning deaths per 100,000 population 3X
more deaths in low-income and low per capita income countries.
In low- and middle-income countries > 90% occur in rivers, lakes, wells, at home, and pools.
TOP 10 causes of death for ages 5
to 14.

37 deaths every hour.


Mortality rate
<1.3 per 100,000 pop.
Unknown mortality

Mortality rate > 3.9 per 100,000 pop.
Mortality rate
1.3-3.9 per 100,000 pop.
(*) Preventing drowning: an implementation guide World Health Organization, editors. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2017.



17
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
DROWNING PROBLEM in the World (2)
The United Nations anticipates an increase in drownings in the coming years if there is no drastic intervention involving prevention measures.
Alcohol is one of the risk factors
• Drowning is the leading cause of death in males aged 5 to 14 and the 5th leading cause among females.
• In the USA, it is the second leading cause of unintentional death in the 1 to 14-year-old age group.
• In children aged 1 to 4 years, drowning is the second leading cause of trauma-related death in South Africa and the first in Australia.
South America#
Major risk factors:
• Age under 14 Years
• Alcohol use
• Low income
• Low education
• Rural ethnicity
• Risky behaviour
• Lack of supervision
• Epilepsy (15 to 19 times).






• South America represents 6% of the world's population (430 million in 2022)
• 3,5% of the total land area on the planet.
• 3% of all unintentional drowning deaths.
(#) Data only includes unintentional deaths





Country N n/100,000 pop 1 Brazil 4833 2.4 2 Colombia 1700 3.8 3 Argentina 600 1.7 4 Peru 1100 4.2 5 Venezuela 800 2.9 6 Chile 500 3.1 7 Ecuador 600 4.3 8 Bolivia 500 6 9 Paraguay 100 2 10 Uruguay 100 2.2 11 Guiana Doesn't inform 12 Suriname Doesn't inform Total 11.696 3.3
18
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
DROWNING PROBLEM in BRASIL
Drownings in Brazil do not differ from the rest of the world, but because it has one of the largest bathable water areas throughout the year, it has the highest number of water rescues and one of the highest numbers of deaths on the planet.
Despite all the frightening data in our country, drowning mortality has been declining in Brazil in the last 43 years (1979-2022) in absolute and relative number (deaths/100,000 population), conferring a reduction in the number of deaths and in the risk of aquatic incidents of more than 50%. This points to the correctness of the measures taken to combat these tragedies – PREVENTION.


Drownings in Brazil are shocking, but they represent only the "tip of the iceberg".
There is daily news of an acquaintance who was healthy and too young to die, surrounded by immense family resentment as to why this tragedy was not prevented.







19
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
5.488
THE DROWNING PROBLEM IN BRAZIL
Drowning is one of the leading causes of death in children and young adults in Brazil.

In 2022, drowning in Brazil was:
• 2nd leading cause of death for ages 1 to 4,
• 4th leading cause of death for ages 5 to 24, and
• 5,488 Brazilians (2.6/100,000 population) died from drowning.


It is estimated that 94% of aquatic incidents in the world are UNKNOWN.
PREVENTION is the most effective tool in the fight against drownings!
Why is it so difficult to convince managers to invest in PREVENTION?
IGNORANCE of the seriousness of the problem, such as the number of people who are subjected to the risk of aquatic incidents on a daily basis and the human and financial costs of these tragedies (fatal or not) are the main reasons.
Although the Ministry of Health's database (DATASUS) provides excellent information with a gap of only 18 months, the system is only able to report cases related to deaths and hospital admissions and excludes all occurrences of water rescues and non-fatal cases that did not require hospitalization.






20
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM IN BRAZIL - Who and When?
The highest risk of death by drowning occurs in the age range of 15 to 49 years (57%)
• 3 children drown daily. A total of 1,397 per year
• Of all drowning deaths, 40% occur before the age of 29 yo.
• Swimming pools and homes are responsible for 4% of all drowning fatalities, but predominantly affect (65%) the age group of 0-9 years old.
• On average, men die 6 times more often than women from drowning, 16 times more in the 20-24 age group.
Season of the year and time of day
• 41% of drownings occur in the months of December to March and the rest are distributed equally over the other 8 months
• More than 65% occur on weekends and holidays.
• More than 50% occur between 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m.

There are variations in the age and location of drownings
• Children aged 1 to 9 drown more often at home due to falls into pools, ponds, toilet, laundry area, and their surroundings.
• Children who know how to swim, drown more often due to suction incidents by pool pumps.
• Children over 10 years old and adults drown more in natural waters such as rivers, dams and beaches.







100% in children, an arm's
in the presence
lifeguards! 21 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
ATTENTION
length even
of
THE DROWNING PROBLEM IN BRAZIL – Vulnerabilities
Drowning deaths do not correlate with the level of education (2022).
Schooling and deaths from drowning in Brazil
Escolaridade: Ignorado
Escolaridade: 12 anos e mais
Nenhuma
Marital Status 2022

Casado Solteiro Ignorado





22 Mortality – RACE - 2022 Population 213.317.639 % N No. drowning deaths Deaths per 100,000 % of deaths Browns 47,4 100.899.243 3267 3,2 59,5 White 43,2 92.366.538 1533 1,7 27,9 Black 8 17.065.411 478 2,8 8,7 Yellow (or Asian) 1 2.133.176 16 0,8 0,2 Indigenous 0,4 853.271 97 11,4 1,8 Ignored 97 Total 100 213317639 5488
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800
Population varies according to the source and period of analysis and it is common to find people who identify with more than one racial category.
Escolaridade:
Escolaridade: 1 a 3 anos Escolaridade: 4 a 7 anos Escolaridade: 8 a 11 anos
Série1 Série2
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM IN BRAZIL – DIVING Trauma
Among all types of diving trauma, the cervical in shallow waters is usually a disastrous situation in a matter of minutes.
A 10-year study of SOBRASA in Brazil from 2013 to 2022, using the ICD W16 (Diving jump or falling into the water causing trauma other than drowning or submersion), reveals:
• The most affected age was between 15 and 44 years (76%) and 95% were men.
• Total dive trauma was 4,986.
• 503 deaths due to diving (10%), 28% (143) before reaching the hospital or Emergency Care Unit (ECU).
• 4,843 people were hospitalized, on average for 5.8 days, with a total hospital cost of US$ 1.959.472 and in-hospital mortality of 7.4% (360 people)
• The risk of diving injury in the general population without considering exposure was 0.24/100,000 population. The South region stands out with a 4 times higher risk.
Notes: Only cases registered as hospital and deaths were included, excluding all minor injuries that did not require care by the Health System (SUS) system or that had hospitalizations in private health without charge/notification to the SUS system.
Diving trauma in shallow water can be avoided by entering the water feet first.

Although the risks of diving trauma are lower, the prognosis and costs are unacceptable and justify a preventive campaign throughout the country.

In 2022, there were 618 diving traumas with 32 deaths, 4 of them before reaching the hospital/ECU. A total of 614 Brazilians were hospitalized, with a mortality rate of 4.6% (28).




23
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM IN BRAZIL – Natural Disasters
In an analysis of the last 31 years (1991 – 2021) of disasters in Brazil, those directly related to drownings (floods, flash floods, and inundations) have had the most significant impact on society, as summarized below :
• 28% of all occurrences
• 2,616 deaths (57% of all occurrences)
• 77% of the displaced population
• 25% of those affected by disasters
• Damages in the order of US$ 15 billion (65%)
• Losses of US$ 12,8 billion (15%)
DISASTERS RECORDED IN BRAZIL FROM 1991 TO 2021

Source: http://atlasdigital.mdr.gov.br/paginas/mapa-interativo.xhtml - Microdata tabulated by Col. BM Edemilson Barros - CBMPR
In the same period of the last 31 years (1991 – 2021), there were 207,296 drowning deaths in Brazil. If we deduct this number from the 2,616 related to floods, flash floods, and inundations, we have drowning (204,680) as a mortality rate 45 times higher than all disasters combined.





24
TYPE OF DISASTER OCCURRENCES DEATHS IDPs/EVs1 AFFECTED DAMAGE (billion R$)2 LOSSES (billion R$)3 FLOODING 1.526 121 409.310 3.369.027 4.97 3.33 FLOODS 9.153 1.872 2.377.862 26.354.830 44.99 36.41 INUNDATION 5.650 623 3.624.597 20.150.119 23.99 24.85 EROSION 614 6 44.575 1.768.202 2.42 1.16 DROUGHT AND DRYNESS 28.007 210 50.035 123.112.445 0.66 309.38 HAIL 1.780 28 360.727 3.146.021 3.77 6.21 FOREST FIRE 1.323 0 1.238 3.653.747 0.24 1.40 LANDSLIDES 1.261 615 236.641 4.214.109 14.73 2.20 HEAT WAVE AND LOW HUMIDITY 126 0 0 1.131.649 0 0.17 COLD WAVE 206 2 6.398 529.881 0.52 1.17 TORNADO 91 17 22.448 318.125 0.33 0.54 STORMS AND CYCLONES 3.640 175 339.487 10.817.418 3.59 9.72 HEAVY RAINFALL 3.453 521 799.685 22.891.04 14.25 24.91 OUTROS 751 394 32.842 3.881.780 0.37 1.53 TOTAL 57.581 4584 8.305.845 202.447.353 114.21 423.04 OBSERVATIONS
Internally Displaced Persons: people whose homes have been destroyed or damaged by disasters and who need to stay in temporary shelters
Evacuees: people whose homes have been damaged or destroyed but who do not necessarily need temporary shelter
Damage: the human, material or environmental, physical or functional losses that may result if control over the risk is lost 3. Losses: These are the economic and social losses resulting from disasters. 2 and 3: Data from 1995 onwards (corrected figures)
1.
1.
2.
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
-
Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
DROWNINGS
What's happening?
THE DROWNING PROBLEM - Where and How?

Estimated location of drowning deaths in Brazil (SOBRASA - 2022)

In 2022 – 5,488 deaths
UNINTENTIONAL DROWNING (88.1%) 2.3/100,000 population
W65 - Drowning in bathtub – 0,13%
W66 - Drowning by falling into bathtub – 0%
W67 – Drowning in a Swimming pool – 2,8%
W68 - Drowning due to falling into swimming pool – 1,3%
W69 - Drowning in natural waters – 41,1%
W70 - Drowning by falling into natural waters – 3,6%
W73 - Other specific drownings – 3,8%
W74 - Drowning with unspecified location – 34%
V90 – Vessel incident causing drowning – 1,1%
V92 – Drowning during water transport without vessel accident – 0,3%
Y21 - UNKNOWN INTENT (7,8%)

(4.1%)




Natural waters
89,9% Freshwater – 76,3% 30% rivers with currents 19% dams 8,3% river backwaters 6% Ponds 7% inundations 3% bay 1,5% Waterfalls 1,5% Streams Ocean Beaches – 13,6% Unnatural waters 8.7% 1% toilets, water tanks, buckets and similar items 2% river water gallery 4,1% Swimming pools 1,7% well
–
Vessels - 1,4%
INTENTIONAL
X71 - Suicide – 3% X92 - Homicide – 1,1%
25 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – Regions and States of Brazil
In 2022, the Southeast region had the lowest death risk (1.8/100,000 population) of deaths due to drowning and the North region had the highest risk (4.3/100,000 population).
States of Brazil - Deaths/100,000 population - 25-Year Valuation (1998-2009 e 2010 a 2022)
Reduction, Unchanged or increase in MORTALITY (*)

Comparing 2 distinct periods of mortality per 100,000 population in the states (Period 1 (1998 to 2009) and Period 2 (2010 a 2022)
• 35% reduction in drowning mortality in Brazil in 25 years. In analysis of the average among the 27 Federative Units:
• Reduction in the number of deaths in 21 states,
• 4 remained unchanged, and
• 2 increased mortality.

Emphasis
David Szpilman. Tabulated data based on the Mortality Information System (SIM) – year 2024 - Ministry of Health - DATASUS – accessed in February 2024. (*) For changes in reduction or increase, we consider significant values greater than 10%. All cases of drowning (intentional or unintentional) were considered Brazilian






Highest reduction rates: SP (68%), DF (67%), RJ (63%), PE (57%), PR (54%), RS (55%), SC (51%) e RR (44%).
REGIONS – year 2022 Cases % Relative death Pop 5.488 100 2,554595 214828540 SOUTH 701 12,773 2,290397 30606047 SOUTHEAST 1646 29,993 1,824197 90231492 NORTH 832 15,16 4,348305 19133894 NORTHEAST 1887 34,384 3,256181 57951331 CENTRAL WEST 422 7,6895 2,496188 16905776 26
in state mortality (% de óbitos/100.000pop)
Increase: Maranhão (19%) e Pará (16%).
TOTAL Percentage (%) achieved Brazil 34,51 Reduction AC 18,36 Reduction AL 38,44 Reduction AP 18,12 Reduction AM -1,32 Unchanged BA 8,632 Unchanged CE 32,58 Reduction DF 66,75 Reduction ES 49,98 Reduction GO 34,59 Reduction MA -19,1 Increase MT 40,47 Reduction MS 51,17 Reduction MG 29,17 Reduction PA -16,4 Increase PB 24,67 Reduction PR 54,45 Reduction PE 57,44 Reduction PI 4,668 Unchanged RJ 62,69 Reduction RN 52,88 Reduction RS 54,87 Reduction RO 48,03 Reduction RR 43,58 Reduction SC 50,77 Reduction SP 68,42 Reduction SE 52,07 Reduction TO -4,96 Unchanged
- What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS





Evolution in the reduction of mortality per 100,000 population in the states, over 44 years
In 2022, on average, the Federal District had the lowest death rate per resident population (1.3/100,000), followed by São Paulo (1.5) and Rio de Janeiro (1.6). The states of Amapá (5.9), Amazonas (5.1), and Roraima (5.0) had the highest rates.

In partnership with:







27 Deaths / 100.000 pop. < 2 2 a 3 3 a 4 4 a 5 > 5
AC AM RR AP PA RO MT MS GO TO MA PI BA MG SP PR SC RS SE AL PE PB RN CE ES RJ DF Brazil
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – Map of the States (2022)
Óbitos / 100.000 hab 1979 1990 2010 2022 BRAZIL 5,42 5,27 3,45 2,55 Acre (AC) 4,06 3,45 4,36 3,04 Alagoas (AL) 3,6 4,18 5,54 3,28 Amapá (AP) 12,2 9,35 8,36 5,93 Amazonas (AM) 5,85 4,76 6,17 5,14 Bahia (BA) 4,1 4,23 4,47 3,58 Ceará (CE) 2,08 2,76 4,46 3,50 Distrito Federal (DF) 4,6 3,98 0,89 1,27 Espírito Santo (ES) 9,68 8,14 4,84 3,94 Goiás (GO) 3,25 3,43 3 2,38 Maranhão (MA) 1 1,55 2,62 3,10 Mato Grosso (MT) 3,4 4,74 5,24 3,46 Mato Grosso do Sul (MS) 3,43 6,61 4,45 2,89 Minas Gerais (MG) 6,38 6,12 3,18 2,19 Pará (PA) 4,86 3,63 4,33 4,17 Paraíba (PB) 1,44 3,04 3,98 3,48 Paraná (PR) 5,58 6,19 3,49 2,50 Pernambuco (PE) 4,67 4,79 3,97 2,67 Piauí (PI) 2,39 1,93 3,72 3,61 Rio de Janeiro (RJ) 7,65 5,76 1,88 1,64 Rio Grande do Norte (RN) 1,45 2,07 3,76 2,64 Rio Grande do Sul (RS) 6,38 5,73 3,48 1,91 Rondônia (RO) 7,48 10,6 4,86 3,27 Roraima (RR) 3,87 7,84 4 5,07 Santa Catarina (SC) 7,17 7,48 3,79 2,54 São Paulo (SP) 6,91 6,59 2,61 1,53 Sergipe (SE) 3,49 5,42 4,69 3,05 Tocantins (TO) ---- 1,33 5,06 3,94 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
- What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
DROWNINGS
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – Tourism (2022)
3% of all drowning deaths are tourists
Where it comes from?
19% São Paulo
8% de Minas Gerais
7% Rio Grande do Sul
5% Paraná
others
Necessary Intervention?
Education in the state of origin

PREVENTION IS EDUCATION
Kim at school

Places of greatest OCCURRENCE of tourist drowning?
10% Santa Catarina
5% no Pará
5% no Rio de Janeiro
5% Espírito Santo
Others

Necessary Intervention?
More investments in Active Prevention (signaling) and Reactive Prevention (lifeguards)










Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
28
partnership with:
- What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
In
DROWNINGS
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – RESCUES AND HOSPITALIZATIONS
A total of 1,565,699 interventions by lifeguards were studied from 2009 to 2015 (5 seasons on the beach of Santa Catarina).

1. Preventive actions - 1,563,300 (99,8%).
2. Recognize a person in a stress/distress situation and rescue them - 2,044 (0,1%).
3. Need for medical assistance for respiratory symptoms, isolated respiratory arrest, or cardiorespiratory arrest – 355 (0,02%)
Estimated incidence of 1 rescue for 4,227 people on the beach, 1 drowning for 24,338 interventions and 1 Resuscitation for 617,142 on beaches guarded by lifeguards.
Of the 2,044 rescues, 14 (0.7%) required respiratory or cardiorespiratory resuscitation. Among all rescues; Grade 1=234 (65,9%); Grade 2=78 (22%), Grade 3=22 (6,2%), Grade 4=7 (2%), Grade 5=4 (1,1%), Grade 6=10 (2,8%).
Considering all interventions performed by lifeguards in a fully operational emergency system, the incidence of resuscitation required was one in every 112,000 actions (0,0009%).

Szpilman D, Oliveira RB, Mocellin O, Webber J. Is drowning a mere mater of resuscitation? Resuscitation 129 (2018) 103-106.




29
1563.300 99,9% 2.044 (0,1%) 355 (0,02%)
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM - Socioeconomic Assessment
Drowning does not choose race, social or economic class and affects everyone. However, access to good education, directly related to income in our country, can reduce its occurrence.

On average, each drowning with death costs
US$ 42,084.16
The relationship between per-capita income (PCI) and the number of deaths in Brazil (2006) shows:
• States with incomes lower than $6,877 show higher incidence of drowning deaths.
• The Federal District, with the highest PCI in the country (US$ 22,863) has one of the lowest risks of death by drowning.
Costs of drowning in Brazil
It quantifies the impact on society and can optimize the allocation of resources in public health policies, direct funds to research, and identify the diseases that most compromise the health budget.
In an assessment from 2008 to 2011, it was identified:

On average, Brazil spends US$240 million on drowning deaths

• 34,639 aquatic incidents recorded in the DATASUS system, of which 95.4% were drownings.
• Of this total, 27,185 people died (78.5% mortality), of which 99% were in the pre-hospital environment.
• 7,674 people hospitalized, consuming 36,001 days of hospital stay (average of 6.6 days/hospitalization) with a total cost of US$ 1,689,197.24.
• The estimated cost for the Supplementary Health System (SSS) was US$ 422,299.31.
• The results of the estimate of the total direct and indirect cost (*) in the period from 2008 to 2011 were $1.3 billion dollars.
(*) Direct costs are those resulting from interventions. Indirect costs include lost productivity associated with absenteeism or early mortality.






30
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – Brazilian Municipalities (2021)
With a total of 5,570 Brazilian municipalities, death by drowning affected 2,227 of them (40%).
The occurrence of deaths in Brazilian municipalities presents a huge variation, from zero deaths by drowning in 3,343 Brazilian municipalities to 196 deaths per 100,000 population in Porto Rico – PR. The list of all municipalities, their absolute death rates and risk of drowning per inhabitant in the year 2022 can be seen in the next pages of state description.
Below are the 10 municipalities with the highest death rates per 100,000 population.

It is important to highlight the impossibility of accounting for the floating population (vacations and summer) in coastal/beach areas where some municipalities can multiply their population by up to 100 times, the bias of the local seasonality analyzed (dry spells, natural disasters such as floods, shipwrecks), as well as in cities with low population, where few deaths result in a high death rate per inhabitants. These are bias factors in the evaluation of the data.





31
Deaths/100,000 pop Population Deaths Municipality 195,77 2554 5 412020 PORTO RICO – PR 148,03 1351 2 430066 ANDRE DA ROCHA - RS 113,96 1755 2 130210 JAPURA - AM 92,25 1084 1 432235 UNIAO DA SERRA – RS 85,80 2331 2 430635 DEZESSEIS DE NOVEMBRO – RS 83,82 2386 2 291995 MAETINGA - BA 81,10 2466 2 430558 COLINAS – RS 80,74 2477 2 520710 DIORAMA – GO 80,19 2494 2 315870 SANTANA DO GARAMBEU - MG 77,68 5149 4 412640 SERTANEJA – PR Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Acre (AC)

Number of deaths: 28 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.04
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 56%
Tourist deaths = 0
Men die 6.5 times more often from drowning
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 18.36%

Alagoas (AL)
Number of deaths: 111 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.3
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 51%
Deaths of tourists from Alagoas in other states = 2
Men die 6 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 38.44%


Download more information about the state and municipalities




32
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022) Amapá(AP)
Number of deaths: 53 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 5.09
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 81%
Deaths of tourists from Amapá in other states = 4
Men die 4.9 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 18.12%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Amazonas (AM)

Number of deaths: 223 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 5.15
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 76%
Deaths of Amazonian tourists in other states = 3
Men die 7 times more often from drowning
Increase in mortality in the last 25 years = 1.32%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




33
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Bahia (BA)

Number of deaths: 539 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.58
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 55%
Tourist deaths in Bahia = 11
Men die 7 times more often from drowning
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 8.63%

Number of deaths: 326 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.50
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 69%
Tourist deaths in Ceará = 5
Men die 9.8 times more often from drowning
Ceará (CE)

Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 32.58%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




34
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022) Brasília (DF)
Number of deaths: 40 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 1.27
Deaths of Brasilienses in other states = 4
Men die 4 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 66.75%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Espírito Santo (ES)

Number of deaths: 164 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.94
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 65%
Tourist deaths in Espírito Santo = 8
Men die 6.8 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 49.98%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




35
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Goiás (GO)

Number of deaths: 174 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.38
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 39%
Tourist deaths in Goiás = 3
Men die 5 times more often by drowning
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 34.59%

Number of deaths: 223 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.10
Maranhão (MA)
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 48%
Tourist deaths in Maranhão = 0
Men die 6.6 times more often from drowning
Increase in mortality in the last 25 years = 19.1%


Download more information about the state and municipalities




36
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024

Professor Polônio



In July 2023, SOBRASA created Professor , an octopus, leader of the volunteer efforts on the World Drowning Prevention Day, in tribute to Professor Antônio Santos, Head of the POOL+SAFE Department, for all his effort and dedication to the mission of reducing drownings. His eight arms represent his constant attention to everyone around him, both in and out of the water.



2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Number of deaths: 125 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.46
Mato Grosso (MT)
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 40%
Tourist deaths in Mato Grosso = 3
Men die 4.6 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 40.47%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Mato Grosso do Sul (MS)

Number of deaths: 83 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.89
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 46%
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Deaths of Mato Grosso do Sul residents in other states = 2
Men die 4.5 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 51.17%





38
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Minas Gerais (MG)

Number of deaths: 472 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.19
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 30%
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Deaths of tourists from Minas Gerais in other states = 14
Men die 5.5 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 29.17%

Pará (PA)
Number of deaths: 370 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 4.17
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 70%
Tourist deaths in Pará = 9
Men die 6.5 times more often from drowning
Increase in mortality in the last 25 years = 16.4%

Download more information about the state and municipalities





39
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Paraíba (PB)
Number of deaths: 142 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.48
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 36%
Deaths of tourists in Paraíba = 1
Men die 6.4 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 24.67%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Paraná (PR)

Number of deaths: 292 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.50
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 34%
Deaths of tourists from Paraná in another state = 8
Men die 5.3 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 54.45%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




40
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Pernambuco (PE)

Number of deaths: 260 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.67
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 56%
Tourist deaths in Pernambuco = 7
Men die 9.8 times more often from drowning
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 57.44%

Number of deaths: 119 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.61
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 27%
Piauí (PI)

Deaths of tourists from Piauí in other states = 7
Men die 4.9 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 4.66%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




41
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Rio de Janeiro (RJ)
Number of deaths: 289 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 1.64
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 63%
Tourist deaths in Rio de Janeiro = 10
Men die 3.7 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 62.69%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Rio Grande do Norte (RN)

Number of deaths: 95 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.64
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 30%
Deaths of tourists in RN = 0
Men die 7.6 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 52.88%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




42
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Rio Grande do Sul (RS)

Number of deaths: 220 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 1.91
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 24%
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Deaths of tourists from Rio Grande do Sul in other states = 11
Men die 5.8 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 54.87%

Number of deaths: 60 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.27
Rondônia (RO)

Municipalities with drowning deaths = 42%
Deaths of tourists from Rondônia in another state = 1
Men die 6.5 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 48.03%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




43
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Number of deaths: 34 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 5.07
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 53%
Tourist deaths = 0
All of the deaths were men
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 43.58%

Download more information about the state and municipalities

Santa Catarina (SC)

Number of deaths: 189 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 2.54
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 34%
Tourist deaths in SC = 17
Men die 5.3 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 50.77%

Download more information about the state and municipalities




44
Roraima (RR)
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
São Paulo (SP)

Number of deaths: 721 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 1.53
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 35%
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Deaths of tourists from São Paulo in another state = 32
Men die 13 times more often from drowning
Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 68.42%

Number of deaths: 72 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.05
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 49%
Tourist deaths = 0
Men die 7 times more often from drowning
Sergipe (SE)

Reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = 52.07%
Download more information about the state and municipalities





45
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
THE DROWNING PROBLEM – by State (2022)
Tocantins (TO)
Number of deaths: 64 Brazilians
Deaths/100,000 population = 3.94
Municipalities with drowning deaths = 30%
Deaths of tourists in TO = 5
Men die 4.3 times more often from drowning
Increase in mortality in the last 25 years = 4.96%


Notes:
Highest number of drowning deaths: São Paulo
Highest number of deaths/100,000 population = Amapá
Lowest number of deaths/100,000 population = DF
Largest number of municipalities with deaths by drowning = Amazonas
Highest number of tourist deaths in the state = São Paulo
Highest number of tourist deaths in the state = Santa Catarina
Highest proportion of men drowning = São Paulo
Highest increase in mortality in the last 25 years = Maranhão
Largest reduction in mortality in the last 25 years = Brasília






46
Download more information about the state and municipalities
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024





Become a volunteer and help save lives through prevention programs.
In partnership with:



47

Choose one action or programme that better impact your local problem
Any action can save a life, no matter how small it may seem Implement and re-evaluate

THE
TACKLING
PROBLEM
Brazilian Lifesaving Society - Sobrasa
48
1 3 2 Understand the DROWNING PROBLEM in your area Multiply Prevention
simple actions Transform reality and Reduce Drownings
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
Your Results
Swimming Pools and Home – Understanding, Planning and Intervening
THE PROBLEM - 4.1% of all drowning deaths in Brazil
• 65% of all drowning deaths among 0 and 9 years olds.
• The occurrence in swimming pools is 20 times higher than other indoor home locations
• The occurrence during leisure in the pool is 2 times more frequent than the accidental fall.
• Home and swimming pools represent 87% of drowning deaths location among 0 to 4 yo
• Children aged 5 to 12 who “can swim” drown more from pump suction in swimming pools (estimated at 28% of the total in swimming pools).
• Location occurrence of pool drowning death: residential (49%), clubs and gyms (10%), schools (7%) and others
• Boys die 2 times more often in swimming pools.
• 44% occur in the summer period, which indicates that impact and seasonal campaigns could be concentrated immediately before this selected period
• The estimated risk of swimming pool death is 1 for every 12,782 swimming pools in a year.
• An average expenditure of US$ 28 million per year with deaths due to drowning in swimming pools is estimated.
• The Southeast is the place with the highest occurrence of drowning in swimming pools death (42%), although the highest risk is the Midwest region, possibly due to a greater number of swimming pools. PLANNING


The POOL+SAFE program created in 2013 by SOBRASA reduces drowning incidents in swimming pools in its surroundings through the education of swimming teachers and students in gyms, schools and clubs.


AVOID SUCTION


PREVENT ACCESS







CLICK on the figure
IMPLEMENTING INTERVENTIONS AND REASSESSING Preparation, Prevention, Reaction and Mitigation 100% EYE ON THE CHILD Education of swimming teachers and students in gyms, schools and clubs. LIFEGUARDS PRESENT (collective swimming pools)
POOL + SAFE 49
HOW TO REACT TO HELP WITHOUT BECOMING A VICTIM 1 3 2 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024
INTERVENTIONS
INTERVENE
KNOW
Beaches - Understand, Plan and Intervene
THE PROBLEM – 13,6% of the total number of drowning deaths in Brazil
• Estimated 746 drowning deaths per year
• The most affected age group is 15 to 49 years old (58%)
• More than 50% of drowned people told they knew how to swim.
• More than 90% occur in rip currents
• Men die an average of 12 times more often.
• 44% occur in the summer period
• Beaches are the places with the highest number of rescues, with an estimated number of more than 56,000 rescues per year
• An estimation of 15,000 lifeguards working on the beaches during the summer.



The prevention program – BEACHES + SAFE, created in 1999 by SOBRASA, reduces drowning on beaches through the education of surfers, water sportsmen and health professionals.
1 3 2
PLANNING INTERVENTIONS
IMPLEMENTING INTERVENTIONS AND REASSESSING Preparation, Prevention, Reaction and Mitigation
Beach with lifeguards on duty only.




Do not enter the water with Red flag. Respect the Signs




If you get caught in a current, stay calm, don't fight, float and wave for help.
NEVER enter the water to rescue, throw a floating material and wait for the professional to arrive



Help a drowned person by calling 193




WATCH THE VIDEO AQUATIC EMERGENCIES
50
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
Rivers, lakes and dams - Understand, Plan and Intervene
1
THE PROBLEM – 69,3% of the total drowning deaths in Brazil
• 10 deaths per day in Brazil.
• Rivers are the places of greatest occurrence, followed by dams
• Drowned death activity were swimming/playing (50%) or fishing (16%).
• The reasons according to witnesses were difficulties while swimming (29%), sudden deepening (18%) and falling from a boat (16%).
• The use of alcohol is responsible for the reduction in risk assessment and overestimation of individual limits in more than 20% of cases.
• The age group over 10 years is the most affected (15-24 years peak-17%).
• Men die on average 6-8 times more often.
• 47% occur on weekends.

3
The prevention program – DROWNING MUNICIPALITIES + RESILIENT - created in 2015 by SOBRASA aims to reduce drowning incidents in rivers, lakes, and reservoirs through safety consultancy to municipalities bordering hydrographic basins, making them more resilient.
2 DROWNINGS

CLIQUE na figura PLAN INTERVENTIONS
IMPLEMENTING INTERVENTIONS AND RE-EVALUATING Preparation, Prevention, Reaction and Mitigation

Share the Flyer

Respect the Signs

If you are going to help: Avoid going into the water to help, CALL 193, THROW floating material and wait for a professional to arrive

100% supervision by those who know how to help, and NEVER enter the water drunk or diving headfirst.

Rapids Rives DO NOT ENTER Non-Rapids Rivers: water at KNEEE LEVEL MAXIMUM.
If boating, WEAR A LIFE JACKET

Help by calling 193

If you are in danger: Keep calm, FLOAT & WAVE FOR help and DO NOT swim against the current.




51
- What's
Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
happening?
Flooding - Understand, Plan and Intervene
THE PROBLEM - 7% of the total number of drowning deaths in Brazil
• In the year 2022, floods, flash floods, heavy rains, and inundations accounted for 35% of all disasters and 90% of all fatalities (270).
• Drowning is the leading cause of death and makes up 18 times the other disasters combined.
• Deforestation, lack of care for garbage and population density contribute to the increase in flooding situations.
• Among the causes of drownings, flooding is the disaster with the greatest economic impact.


The KIM AT SCHOOL program - created in 2010 by SOBRASA, reduces drowning incidents in FLOODS through education in primary schools.
IMPLEMENT INTERVENTIONS AND REASSESS
Preparation, Prevention, Reaction and Mitigation
Prevention is the most efficient way to reduce these occurrences:
• Floods occur very quickly, do not risk your life and that of your family members
• Consult the Civil Defense before choosing, buying or building on a plot of land
• Attention to weather reports and Civil Defense guidelines
• Use tall, off-street trash cans and gutters. 1.










PLAN INTERVENTIONS
on the figure
CLICK
At the sign of rising water levels, pack your valuables.
If there is water in the house, immediately go to higher areas and call 193 or 199.
If there is infiltration, cracks, strange noise, or movement of poles/trees, evacuate the house immediately.
Turn off the power, only use cell phones and batterypowered flashlights. 5. Close the gas, water, and doors and windows of the house. 6. Animals - release them. 7. Broadcast alarm to neighbors 8. Stay away from the water currents.
If caught in a current, float with your belly up and feet in front of you and wave for help. If possible, get a flotation material.
Never try to save someone by entering the water, call 193, throw some floating material and wait for the professionals to arrive. 52
3
CLICK ON THE IMAGES DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
2.
3.
4.
9.
10.
1
2


Become a volunteer and help save lives through prevention programs.

In partnership with:



SOBRASA - Who are we?
Founded in 1995, it represents Brazil at the International Life Saving Federation - ILS.
Board of directors
13 directors, 56 heads of departments, 200 consultants
Present in the 27 states of the federation
4,067 volunteers carry out more than 13 face-toface drowning prevention actions daily at various locations across Brazil
MISSION
Unite Brazil to reduce drownings.

VISION
A world without drownings.
VALUES
Reliability – Determination - Altruism
- Proactivity - generosity


All of them work on a voluntary basis with no perception of fees or allowances.
A 47% reduction in drowning deaths in 43 years (1979-2022) points to the right path in the fight against this endemic.


More than
220,000 followers on social media







54
LEARN MORE...
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
5
REASONS to understand the SOBRASA IMPORTANCE

4
5
1
1
2
3
28 years uniting experts and lifeguards with a single mission: Reduce drownings.
Free drowning prevention programs throughout the country.
Prevention, rescue and first aid protocols, supporting our lifeguards on a daily basis.
Partnership with more than 45 national and international institutions (WHO, ILS, Blue Flag, CBDA, ABRAMEDE, CREF, LIGABOM, National Civil Defense, MGB, EMERGENCY Magazine, ISN, SBAIT, INMETRO among others).
Reliable, determined, altruistic, proactive and generous volunteers, united by a cause.
5

SOBRASA’s interventions with the HIGHEST impact

125 major prevention actions reaching more than 110 million people in Brazil and Latin countries.
2 A portal with more than 3 GB of free technical materials.
4
5
3
Leadership & participation in the main national and international protocols and strategies to combat drowning.
345 scientific papers published in the area of water safety.
2,300 participations in scientific and sporting events.

In partnership with










55
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa



Learn more about our volunteers and programs


MEET our mascots






They help in drowning prevention education!
Download mascots and stickers

LEARN ABOUT our free programs and tools FIND OUT WHO










Highlights
57
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
SOBRASA IS Institutional Video
In partnership with
















58 In partnership with Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
Prevention Programs Discover our tutorials Click to access
Highlights




about the history of our mascots Click to access
Learn
































































&
60
partnership with Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
LEARN ABOUT our free programs and tools Click on the images Drowning prevention comics Freshwater Flooding Pools Beaches How to use the comic books? Freshwater Flooding Online Games Beaches Download
Print Top mensagens Multi-actions (includes several programs) Cartoons AED Courses house Events Prevention Sport
In
Highlights
Get to know our new manual











61 In partnership with Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
Highlights




Discover our collection Click to access

Results from SOBRASA
4.067 Volunteers
4,873 Prevention actions
13 actions per day


314,108 People Directly Reached






SUMMARY 2023

65 students per action (on average)
13,479 hours worked by our volunteers
172,753 children
141,355 adults

942,324 Family Reached





63 In partnership
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
with
Results from SOBRASA

SOCIAL MEDIA

224.758 Social Media Followers







42,459 facebook
107,729 Instagram
16,430 Youtube

11,280 Whatsapp groups
2,532 Telegram group members
14,151 webpage subscriber


SUMMARY 2023
21 million impressions
58,140 Others (X, LinkedIn, Trends, TikTok, Pinterest and others)
37,674 Posts







64 In partnership with Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa

1.563 NEWS TVs, Radios, Newspaper, blogs and others (ATL).


176 million people reached (coverage) ORGANIC MEDIA


US$
2,076,188.95 earned media generated


1,3 bilhão Views





SUMMARY 2023
65 In partnership
Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
with
Results from SOBRASA
SOBRASA Collaborators – 2023






Stay on top of all our preventive work over these 28 years. “



























66
“APPROVED products” (quality) “Gold Seal” (technic-education)
SILVER
- What's
Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
Our PARTNERSHIPS” GOLD
DROWNINGS
happening?
ABOUT THIS BRAZILIAN BULLETIN – 2024
The reality of the data presented here does not highlight a new problem in our country, but an old and serious endemic issue that is little known and publicized in our society.
This Bulletin was prepared by SOBRASA and its Board of Directors 2023-25, in February 2024, based on the year 2022 and some previous information that remained unchanged Its objective is to document the extent of the problem regarding drownings and aquatic incidents in Brazil, as well as to identify causes and propose solutions for prevention, rescue, and mitigation
The fight to reduce these incidents is for everyone who wishes to join this challenge – WATERSAFETY! Therefore, the use of this information and its content can and should be distributed freely and openly, as long as its original structure and due credits are maintained.
Why a 2-year lapse between the current date and the latest year of data available in DATASUS?
The data researched on DATASUS, whether VITAL STATISTICS (mortality) or EPIDEMIOLOGICAL AND MORBIDITY data (Hospital Morbidity of SUS (SIH/SUS)), is manually inputted after the annual closure of death certificates (mortality) and hospitalization charges to the SUS system, which results in a two-year lag. We must emphasize that DATASUS maintains one of the most updated and comprehensive databases on-line in the field worldwide
Our VOLUNTEERS thank you
The preparation of this bulletin required the analysis of 78 different spreadsheets and more than 76 hours of work, voluntarily dedicated to the cause of the reduction of drownings.






67
more...
the arrow to learn more.
Click
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS

In this year of 2024, we have gained many new partners and volunteers, and we are celebrating life at its peak for the reduction of drownings in these 28 years of existence. In this moment of great unity and fight, the entire board of directors wishes to: THANK DHL, the Princess Charlene of Monaco Foundation, and SOSSUL for believing that our mission is not a dream but a reality that transforms the lives of many families across Brazil, from north to south and from east to west, in this vast country that suffers daily from the 15 death and loss of loved ones - THANK YOU VERY MUCH!

THANK all who are with us in this wonderful and successful mission – our 4,000 volunteers.
THANK all who have been with us in this 28-year fight.
Your ADN is in our prevention actions.
You see that person in yellow in the photo?
That's YOU without a doubt!
Words will not reflect all the GRATITUDE for the tireless work of our VOLUNTEERS, nevertheless,
THANK YOU, THANK YOU, and THANK YOU!




68
DROWNINGS - What's happening? Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
References
1. David Szpilman. Data and analysis based on data from the Mortality Information System (SIM) tabulated in Tabwin - Ministry of Health - DATASUS - 2023. Accessed online July 2023. http://www2.datasus.gov.br/DATASUS/index.php, latest data available year 2021
2. Schinda A, Deitos RA, Szpilman D, Carniatto I. Drowning prevention measures directed at a river basin: a new strategy. World Conference on Drowning Prevention - ILS, Malaysia 2015, Book of Abstract, PREVENTION Section, p181. ISBN: 978-0-909689-00-1.
3. Preventing drowning: an implementation guide. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO
4. Szpilman D, Sempsrott J, Schmidt A. Drowning. BMJ Best Practice. Nov 2017. http://bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-gb/657. Last accessed 19 April 2018.
5. Szpilman D, Oliveira RB, Mocellin O, Webber J. Is drowning a mere mater of resuscitation? Resuscitation 129 (2018) 103-106.
6. Szpilman D, Sempsrott J, Webber J, Hawkins SC, Barcala-Furelos R, Schmidt A, Queiroga AC. “Dry drowning” and other myths. Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. 2018 July;85(7):529-535.
7. Szpilman D, Pinheiro AMG, Madormo SR. Drowning perception risk table –World Conference on Drowning Prevention - ILS, Vancouver 2017, Book of Abstract, Data Section, p105. ISBN 978-1-926508-05-4. access at www.wcdp2017.org
8. Szpilman D, Braga F, Schinda A. The five water safety messages customized for different aquatic scenarios –. World Conference on Drowning Prevention - ILS, Vancouver 2017, Book of Abstract, Data Section, p77. ISBN 978-1-926508-05-4. access at www.wcdp2017.org
9. Szpilman David, Tipton Mike, Sempsrott Justin, Webber Jonathon, Bierens Joost, Dawes Peter, Seabra Rui, Barcala-Furelos Roberto, Queiroga Ana Catarina, Drowning timeline: a new systematic model of the drowning process, Am J Emerg Med. 2016 Nov;34(11):2224-2226.
10. Szpilman D, Barroso PAS, Barros E, Mocellin O, Alves JFS, Smicelato CE, Trindade R, Vasconcellos MR, Schinda A, Villela J, Silva-Júnior LMS, Morato M, Lopes W. Drowning prevention – different scenarios needs customization water safety messages and actions. World Conference on Drowning Prevention - ILS, Malaysia 2015, Book of Abstract, PREVENTION Section, p74. ISBN: 978-0-909689-00-1. DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.3506.1200
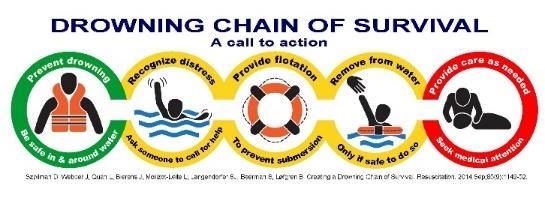
11. Szpilman D, Webber J, Quan L, Bierens J, Morizot-Leite L, Langendorfer SJ, Beerman S, Løfgren B. Creating a Drowning Chain of Survival Resuscitation. 2014 Sep;85(9):1149-52.
12. Schinda A, Szpilman D. Resilient city for drowning program – World Conference on Drowning Prevention - ILS, Vancouver 2017, Book of Abstract, Data Section, p120. ISBN 978-1-926508-05-4. access at www.wcdp2017.org
13. Szpilman D, Mello DB, Queiroga AC, Emygdio RF. Association of Drowning Mortality with Preventive Interventions: A Quarter of a Million Deaths Evaluation in Brazil. International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education. Volume 12 Number 2, Issue 2, 2020.
14. Szpilman D, Palacios-Aguilar J, Barcala-Furelos R, Baker S, Dunne C, Peden AE, Brander R, Claesson A, Avramidis S, Leavy J, Luckhaus JL, Manino LA, Marques O, Nyitrai NJ, Pascual-Gomez LM, Springer L, Stanley TJ, Venema AM, Queiroga AC. Drowning and aquatic injuries dictionary. Resuscitation Plus. Volume 5, March 2021, 100072.
15. Szpilman D & Morgan P., Management for the drowning patient, CHEST October 13, 2020.
16. David Szpilman – Drowning Handbook to Water Emergencies Course 2019. Published online on www.sobrasa.org, March 2023.
17. Sobrasa Tutorials: Volunteer Action Manual, Kim at School, Swimming Pool + Safe, Sobrasa Kid's, Surf-Sage, Instructions. Published online on www.sobrasa.org, May 2023
HOW TO REFERENCE THIS BULLETIN
David Szpilman & Sobrasa Board 2022-25.
Drowning – Epidemiological Bulletin in Brazil 2024. Considering using microdata from DATASUS. Brazilian Lifesaving Society SOBRASA
Posted online at http://www.sobrasa.org, February 2024.
Reviewed by Dr. Lúcia Eneida Rodrigues, Prof. Eduardo Santos and Col. Edemilson Barros. DROWNINGS




- What's
Brazil Bulletin – 11th edition - 2024 Brazilian Lifesaving Society Sobrasa
happening?
















































































































































































































































































































































































































